Bolbitis sinensis (Baker) K.Iwats.
Family
Dryopteridaceae
Nomenclature
Bolbitis sinensis (Baker) K.Iwats., Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 18: 49. 1959; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 3(3): 85. 1965; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 5: 90. 1967; Hennipman, Leiden Bot. Ser. 2: 202, f. 53 & 54. 1977; Holttum, Fl. Males., Ser. II, Pterid. 1: 325, f. 27h. 1978; Tagawa & K.Iwats., Fl. Thailand 3: 318, f. 26.1–4. 1988; Boonkerd & Pollawatn, Pterid. Thailand: 184. 2000. – Acrostichum sinense Baker, Bull. Misc. Inform. Kew 1906: 14. 1906. – Egenolfia sinensis (Baker) Maxon, Proc. Biol. Soc. Washington 36: 173. 1923; Tardieu & C.Chr., Fl. Indo-Chine 7(2): 424, f. 48.1 &48.2. 1941; Holttum, Dansk Bot. Ark. 20: 30. 1961.
Acrostichum appendiculatum var. costulatum Hook., Sp. Fil. 5: 252. 1864. – Polybotrya appendiculata var. costulata (Hook.) Bedd., Ferns Brit. India: pl. 110. 1865; Bedd., Handb. Ferns Brit. India: 426, f. 257. 1883. – Egenolfia bipinnatifida J.Sm., Hist. Fil.: 132. 1875. – Bolbitis bipinnatifida (J.Sm.) K.Iwats., Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 18: 49. 1959, as 'bipinnata', nom. illeg. – Bolbitis sinensis (Baker) K.Iwats. var. costulata (Hook.) Tagawa & K.Iwats., Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 22: 102. 1967; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 5 91. 1967; Tagawa & K.Iwats., Fl. Thailand 3: 319, f. 26.5. 1988; Boonkerd & Pollawatn, Pterid. Thailand: 184. 2000. – Bolbitis costulata (Hook.) Fraser-Jenk., Taxon. Revis. Indian Subcontinental Pteridophytes : 345. 2008. – Type: Burma, Tenasserim, Dawna Range near Moulmein, Parish 60 (holo K).
Description
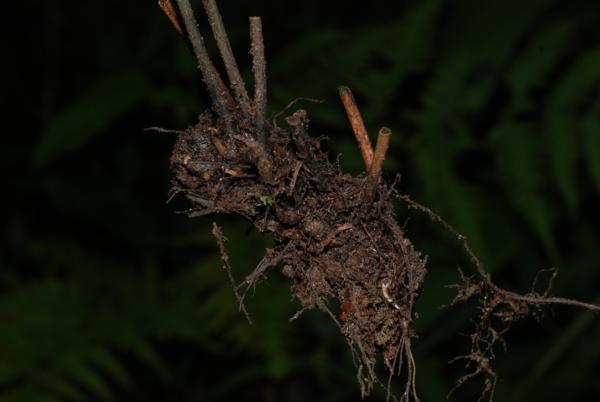
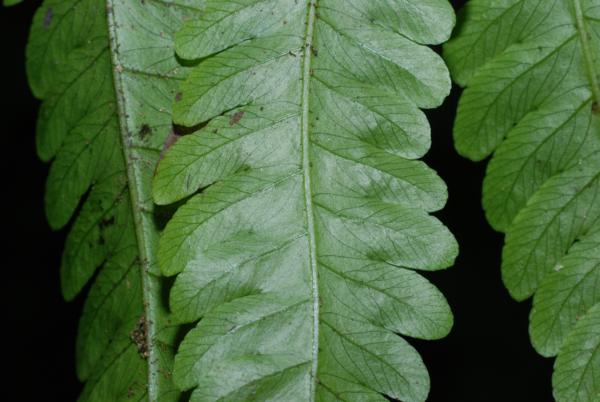
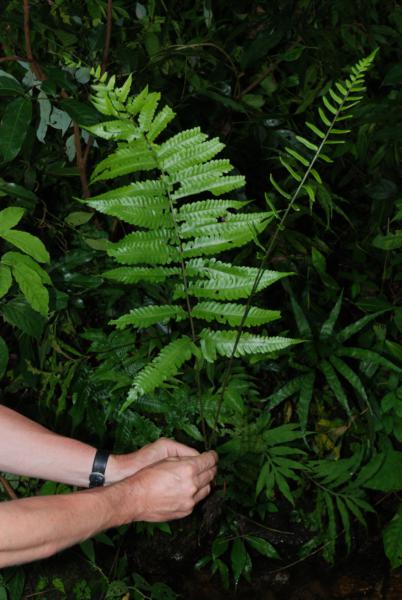
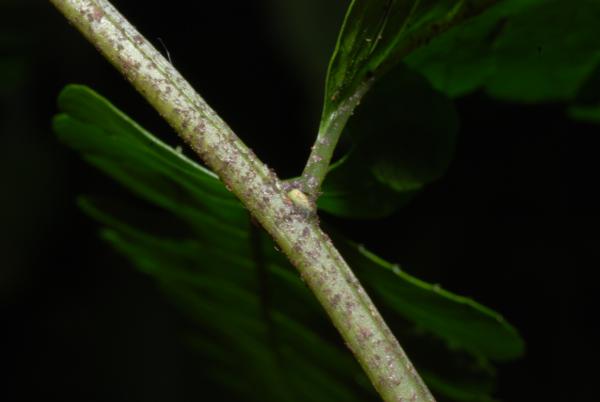
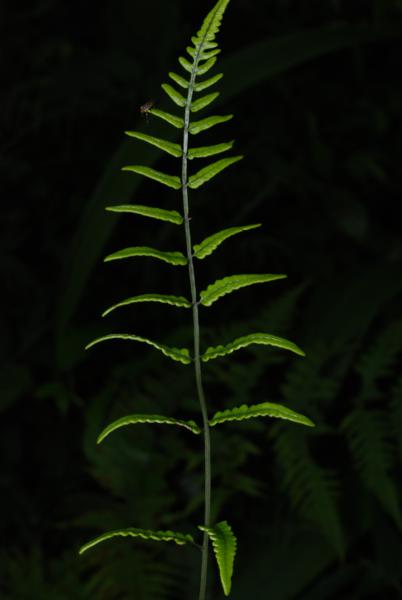
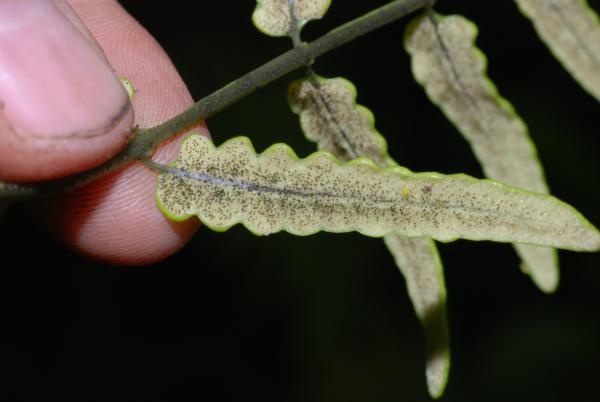
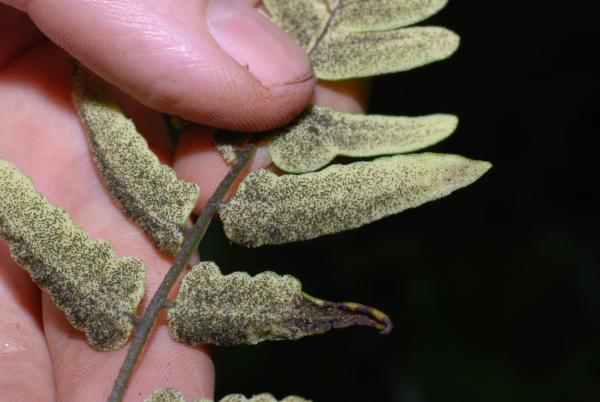
Terrestrial, sometimes lithophytic or epiphytic. Rhizome short creeping; scales greyish-brown, hardly clathrate, narrowly subtriangular with long acuminate apex, entire, up to 4 by 0.8 mm. Sterile frond: stipe 15–30 cm long, scaly at base with brown, appressed, membranous, small, broadly oblong scales; lamina narrowly subtriangular, 25–90 x 12–30 cm, the apex attenuately long-tailed, often viviparous at apex; rachis sparsely scaly, winged in upper part; lateral pinnae 14–40 pairs, basal pinnae the longest, stalked, with or without an enlarged and lobed basal basiscopic pinnule, middle pinnae patent, lanceolate, shortly stalked, upper ones ascending, oblong, moderately acute to rounded at apex, less lobed, adnate at base to form indistinct apical pinna; lobes oblique, rounded at apex, up to 7 mm broad, close to each other; main veins raised beneath, sparsely minutely scaly, veinlets simple or forked, all free; herbaceous to papyraceous, deep green, dark brown when dried. Fertile frond about the same height as or lower than the sterile one; stipe 25–40 cm long; lamina narrower, 15–45 by 5–15 cm; lower lateral pinnae oblong, 1.3–9 x 0.4–2.5 gradually narrowing from base to apex, subtruncate or rounded at distinctly stalked base, rounded to moderately acute at apex, subentire or very slightly waved at margin, terminal pinna narrowly subtriangular with lobed base; veins pinnate, veinlets simple, all free, the apex ending inside the distinct cartilaginous margin; sporangia dispersed on the undersurface, naked.
Distribution in Thailand
NORTHERN: Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Nan, Lamphun, Lampang, Phitsanulok; NORTH-EASTERN: Phetchabun, Loei; SOUTH-EASTERN: Chanthaburi.
Wider Distribution
N India, Burma, SW China and Vietnam.
Ecology
Usually terrestrial on humus-rich slopes in dense mountain forests, sometimes on muddy rocks or even on base of tree-trunks, fairly common at 500–1800 m alt.
Proposed IUCN Conservation Assessment
Least Concern (LC). This variety is widespread and not under any known threats.
Voucher specimens - Thailand
Middleton et al. 4869, Chiang Mai, Doi Suthep-Doi Pui National Park (E); Middleton et al. 4928, Chiang Mai, Doi Inthanon National Park (E); Middleton et al. 5166, Loei, Phu Luang Wildlife Sanctuary (E).
Habit
Habit
Rhizome
Upper urface of sterile frond
Bulbil
Sterile and fertile fronds
Aerophore at junction of rachis and pinna
Spines on upper surface of sterile lamina
Sterile pinnae
Venation in sterile frond
Fertile frond
Upper surface of fertile pinnae
Fertile pinna with young sori
Fertile pinnae with young sori
Older and younger fertile pinnae
Site hosted by the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh. Content managed by Stuart Lindsay, Gardens by the Bay, Singapore and David Middleton, Singapore Botanic Gardens. Last updated 24 January 2012














