Crepidomanes bipunctatum (Poir.) Copel.
Family
Hymenophyllaceae
Nomenclature
Crepidomanes bipunctatum (Poir.) Copel., Philipp. J. Sci. 67: 59. 1938; Ching, Fl. Reipubl. Popularis Sin. 2: 162, pl. 12, f. 8. 1959; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 3(3): 74. 1965; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 5: 41. 1967; Tagawa & K.Iwats., Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 23: 52. 1968; Tagawa & K.Iwats., Fl. Thailand 3: 90. 1979; Tagawa & K.Iwats., Fl. Thailand 3: 613. 1989; Boonkerd & Pollawatn, Pterid. Thailand: 68. 2000. – Trichomanes bipunctatum Poir. in Lam., Encycl. (Lamarck) 8: 69. 1808; Bedd., Handb. Ferns Brit. India: 41. 1883; C.Chr., Bot. Tidsskr. 32: 340. 1916; E.Smith, J. Siam Soc. Nat. Hist. Suppl. 8: 2. 1929; Copel., Philipp. J. Sci. 51: 177, pl. 18, f. 14. 1933; Tardieu & C.Chr., Fl. Indo-Chine 7(2): 63. 1939; Holttum, Rev. Fl. Malaya ed. 1, 2: 99, f. 35. 1955 [‘1954’]; Holttum, Dansk Bot. Ark. 20: 17. 1961; Seidenf., Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 19: 86. 1958.
Trichomanes bilabiatum Nees & Blume, Nova Acta 11: 123, t. 13, f. 2. 1823; C.Chr., Bot. Tidsskr. 32: 34. 1916; Copel., Philipp. J. Sci. 51: 179, pl. 18, f. 5–6. 1933; Holttum, Rev. Fl. Malaya ed. 1, 2: 99, f. 36. 1955 [‘1954’]; Holttum, Dansk Bot. Ark. 23: 229. 1965. – Crepidomanes bilabiatum (Nees & Blume) Copel., Philipp. J. Sci. 68: 59. 1938; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 5: 41. 1967; Tagawa & K.Iwats., Fl. Thailand 3: 90. 1979.
Trichomanes pyxidiferum auct. non L.: Christ, Bot. Tidsskr. 24: 103. 1901.
Trichomanes filicula auct. non Bory: Christ, Bot. Tidsskr. 24: 103. 1901.
Description
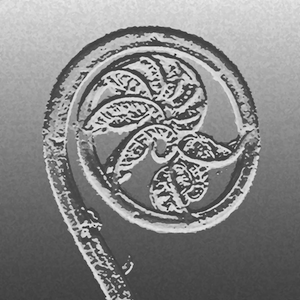
Rhizome about 0.7 mm diam., covered with dark brownish hairs. Stipes (0.2–) 2–3(–4.5) cm long, winged almost to the base, bearing short hairs. Laminae variable in shape and size, ovate to oblong, round to acute at apex, tripinnatifid, usually (2.1–)4–8 cm long, (1.2–)3–5(–5.5) cm wide, often dwarfed with sori; pinnae 5–8 in pairs, the larger ones 1.5–3 cm long, 1–1.5 cm wide, shortly stalked or sessile in the upper ones; pinnules oblong to subdeltoid, with about 10 segments; ultimate segments linear-lanceolate, at a narrow angle to each other, acute at apex, entire and flat at margin; false veinlets marginal, continuous or interrupted, occupying two or more rows of marginal cells, the other striae few to many. Sori on the apices of short axillary lobes; involucre tubular, 1–1.8 mm long, winged, the mouth bilabiate, the lips round to acute, usually as wide as long, receptacles exserted .
Distribution in Thailand
NORTH-EASTERN: Loei; EASTERN: Nakhon Ratchasima; SOUTH-WESTERN: Kanchanaburi; Phetchaburi, Prachuap Khiri Khan; CENTRAL: Nakhon Nayok; SOUTH-EASTERN: Chanthaburi, Trat; PENINSULAR: Chumphon, Ranong, Surat Thani, Krabi, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Phuket, Phatthalung, Trang, Satun, Yala, Narathiwat.
Distribution in Cambodia
Kampot.
Wider Distribution
Old World tropics.
Ecology
On mossy or muddy rocks or on mossy tree trunks in dense forest at various altitudes.
Proposed IUCN Conservation Assessment
Least Concern (LC). This species is widespread and not under any immediate known threat.
Voucher specimens - Thailand
Middleton et al. 4384, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Khao Luang National Park (E); Middleton et al. 5346, Satun, Thale Ban National Park (E); Middleton et al. 5409, Phatthalung, Lan Mom Jui Waterfall (E); Middleton et al. 5472, Satun, Than Plew Waterfall (E); Middleton et al. 5530, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Khao Luang National Park (E); Middleton et al. 5549, Surat Thani, Khlong Phanom National Park (E).
Habit
Fronds with mature sori
Frond apex with sori
Close up of sori
Stipe
Fronds showing intramarginal false veins
Site hosted by the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh. Content managed by Stuart Lindsay, Gardens by the Bay, Singapore and David Middleton, Singapore Botanic Gardens. Last updated 24 January 2012





