Salvinia cucullata Roxb. ex Bory
Family
Salviniaceae
Nomenclature
Salvinia cucullata Roxb. ex Bory in Bél., Voy. Indes Or. 2: 6. 1833; Tardieu & C.Chr., Fl. Indo-Chine 7(2): 543. 1941; Holttum, Rev. Fl. Malaya ed. 1, 2: 621. 1955 [‘1954’]; Holttum, Dansk Bot. Ark. 20: 35. 1961; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 3(3): 89. 1965; Tagawa & K.Iwats., SouthE. Asian Stud. 5: 112. 1967; Tagawa & K.Iwats., Fl. Thailand 3: 604. 1989; Boonkerd & Pollawatn, Pterid. Thailand: 97, 116. 2000; Newman et al., Checkl. Vasc. Pl. Lao PDR: 32. 2007.
Salvinia natans auct. non (L.) All.: Dy Phon, Dictionary of Plants used in Cambodia: 546. 2000.
Description
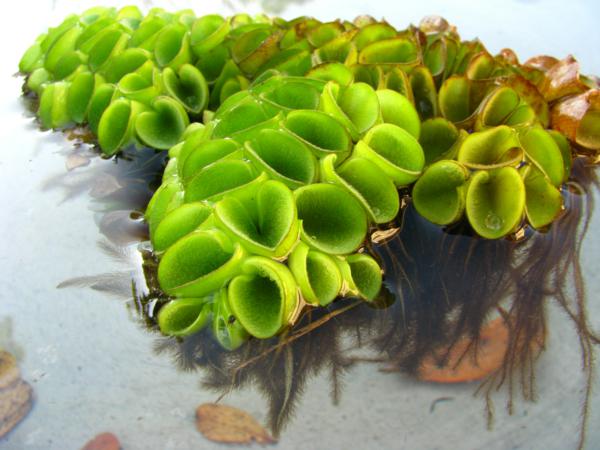
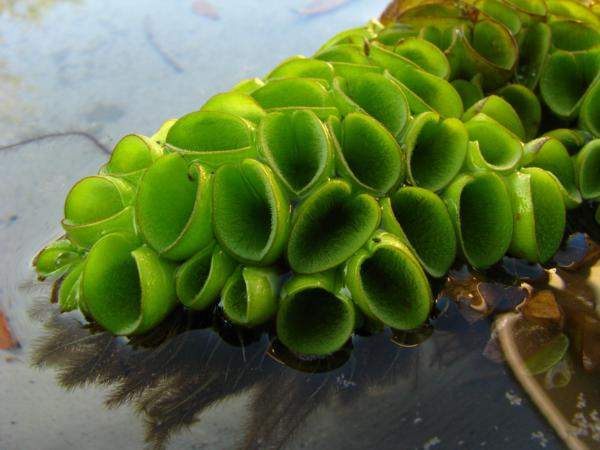
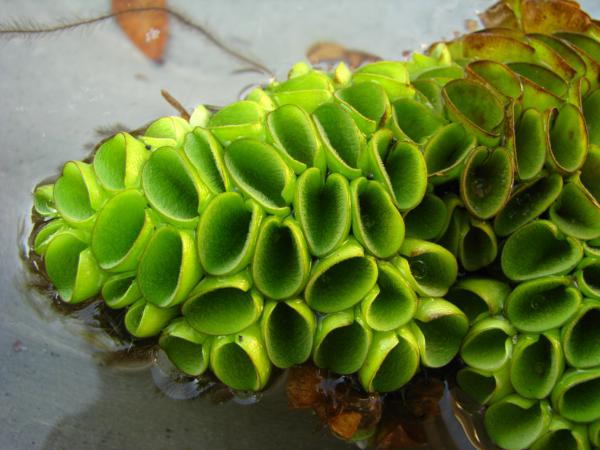
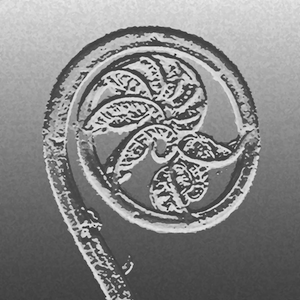
Floating leaves thick but soft, 1.2–1.8 cm long, wider than long, with sides curved upwardly and inwardly to meet the edges; upper surface covered with dense short projections bearing setae; lower surface with a few downy hairs. Sori many on various branches of the submerged leaves.
Distribution in Thailand
NORTHERN: Chiang Mai; SOUTH-WESTERN: Prachuap Khiri Khan; CENTRAL: Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Pathum Thani; PENINSULAR: Surat Thani.
Distribution in Laos
Champasak.
Distribution in Cambodia
Kampot.
Wider Distribution
India, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia to Sumatra.
Ecology
Floating on water in open places.
Proposed IUCN Conservation Assessment
Least Concern (LC). This species is widespread and not under any known threat.
Notes
In Cambodia said to be used to feed pigs (Dy Phon, 2000).
Habit
Habit
Habit
Site hosted by the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh. Content managed by Stuart Lindsay, Gardens by the Bay, Singapore and David Middleton, Singapore Botanic Gardens. Last updated 24 January 2012


